Door to History: New owners of old Union Trust Building hope to find use for bank vault
Wednesday, March 12, 2008
By Sally Kalson, Pittsburgh Post-Gazette
When the Union Trust Building opened Downtown in 1923, its safe deposit vault in the basement was reported to be the largest and strongest in the world — 80 feet long, 45 feet wide, 8 2/3 feet high, with walls 20 inches thick.
Now, 85 years and several bank mergers and sales later, the vault is still an impressive, if musty, catacomb that harkens back to another era. With its rows of burnished bronze cubbies, clanking gates and massive circular 55-ton door, it could easily be imagined as the set of an old bank heist movie starring James Cagney or Edward G. Robinson.
There’s almost nothing left there to steal now. Citizens Bank, which took over the vault from Mellon Bank after buying the latter’s consumer and small business operation in 2001, began notifying depositors several months ago to empty their lock boxes because it was vacating the premises.
Only about 1,800 of 12,000 boxes were in use at that point. Most have been cleared out by their owners, although some unclaimed boxes remain. On March 21, the vault will officially close; any leftovers will be drilled and moved to the Citizens branch across the street for safekeeping while the bank looks for their owners.
Citizens Bank president Ralph Papa, who was with Mellon for many years before the sale, said there was no need to keep the Union Trust vault in operation.
“We have more than 90 branches around the area, and the vast majority have safe deposit boxes,” he said. “There are lots of places for people to move the contents.”
Still, the closing of the storied vault sounds like the end of an era. But the Union Trust Building’s new owners say they are well aware of the basement’s historic nature.
“We’re looking at a number of uses,” said Rick Barreca, CEO of the Mika Realty Group of Los Angeles, which last month paid $24.1 million for the 11-story property.
“Our hope is that we can work with another financial institution in the future that might make use of the vault,” Mr. Barreca said. “It’s really a work of art, a unique facility that I think is irreplaceable. We have a large commitment to the building, and the vault is one of the benefits of owning it.” …..
That’s a sensible attitude, because it’s hard to see how the structure could be removed without tremendous cost and disruption. Mika is considering excavating under the building for a parking garage, but Mr. Barreca said “there’s plenty of room for that without touching the vault.”
Sparse history
Much has been written about the Union Trust Building from the ground up. The edifice is considered by many to be Downtown’s most spectacular, with its ornate Flemish Gothic exterior, 10-story rotunda, circular skylight and the twin “chapels” on the roof that actually house elevator machinery. It takes up the entire city block bounded by Fifth and Oliver avenues, Grant Street and William Penn Place. The design is credited to F.J. Osterling, but was probably conceptualized by Pierre A. Liesch, who worked for Osterling briefly, according to the late historian James D. Van Trump. In 1973, the building was recognized as a historic landmark.
But when it comes to the underground portion, there’s very little on the historical record. However, one article from the Pittsburgh Sun newspaper, dated Nov. 21, 1932, contained a descriptive bonanza.
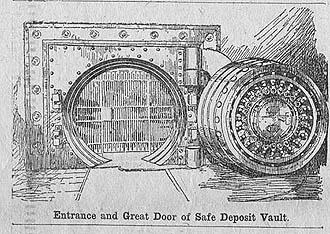
“Great Vault Is World’s Largest” was the Sun headline that introduced the facility to the public. The report included illustrations of the vault opening and its interior and noted that the total weight of the doors and equipment was 5 million pounds.
The report described the vaults as “great fire, burglar, flood and mob proof strongholds,” built of “a double tier of interlocked heavy steel beams, surrounded by and imbedded in solid concrete, lined with the hardest and toughest armor plate.
“Every inch is guarded by electric alarms, and every protective device developed by human genius and skill has been installed to make absolutely safe the possessions deposited in it.
“The material is finished in solid bronze, and the boxes are 26 inches deep and are made of open hearth steel, the doors being one-half inch thick. The portable boxes are aluminum and were made by the Aluminum Company of America.”
The article went on to recommend the “impregnable trunk vault” as the ideal repository for silverware, heirlooms, valuable books and other bulky possessions.
All the more noteworthy is the fact that the vaults were retrofitted, because the building was not designed as a bank. It opened in 1917 as the Union Arcade, built by Henry Clay Frick on land he purchased from the Catholic Diocese of Pittsburgh. At the time, it claimed to be the largest arcade in the world, with 240 shops on the first four floors and 760 office suites on the upper levels.
Six years later, the Union Trust Co. took over more than two acres of floor space, put its name on the edifice and its vault under it. The retrofitting was done by Graham, Anderson, Probst & White, successor of D. H. Burnham & Co., architects of the Frick and Oliver buildings.
The newspaper described the vaults as occupying two levels — nearly 28,000 square feet on the safe deposit floor, and some 20,000 square feet on “the silver vault floor” for paintings, bullion and other heavy possessions.
That left the folks at Citizens scratching their heads, because the vault as it exists today has only one floor. “Nobody seems to know about that second floor,” said spokeswoman Angela Wagner.
The vault is changed in other ways as well. The open central area depicted in the Sun’s 1923 illustration is now crammed full of deposit boxes that were forklifted over from Mellon Bank’s Smithfield Street location after that building was sold in 1999 and made into a Lord & Taylor department store that closed five years later.
It’s hard to say for sure if the vault anteroom floor is original. The surface comes up higher than the bottom of the vault door, so the floor must be dropped by means of a long pole and lever to clear the way for swinging the enormous door open or closed. That may be depicted by the curved line in the illustration, but it’s difficult to tell.
The Union Trust Co. merged with Mellon Bank in 1946 to form Mellon National Bank & Trust Co. The building was rechristened Two Mellon Bank Center in the 1990s, but most Pittsburghers never stopped calling it the Union Trust Building.
Mellon — now Bank of New York Mellon — left the premises in 2006, and the structure is virtually empty except for Larrimor’s on the street-level corner of Grant and Fifth. Mika Realty hopes the high-end men’s clothier will remain, and CB Richard Ellis is charged with attracting new retail and office tenants.
As for the vault, it’s not going anywhere.
Sally Kalson can be reached at skalson@post-gazette.com or 412-263-1610.
First published on March 12, 2008 at 12:00 am